Using the Clonalg
Access the Jupyter notebook with the code available here!
Run notebook online via Binder:
Clonalg to the Rastrigin Function
The Rastrigin function is a multimodal, non-convex function with many local minima, making it an excellent benchmark for optimization algorithms, learn more. The function is defined as:
Where:
- n is the problem dimension
- xᵢ ∈ [−5.12, 5.12] for each dimension
- Global minimum: f(0,0) = 0
Import of the required libraries
# Importing the Clonal Selection Algorithm (CLONALG)
from aisp.csa import Clonalg
# Libraries for data manipulation and numerical calculations
import numpy as np
# Data visualization
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Problem Definition
problem_size = 2
bounds = {'low': -5.12, 'high': 5.12}
def rastrigin_fitness(x: np.ndarray) -> float:
x = np.clip(x, bounds['low'], bounds['high'])
n = len(x)
result = 10 * n
for i in range(n):
result += x[i]**2 - 10 * np.cos(2 * np.pi * x[i])
return result
Algorithm configuration
# Optimized Clonalg configuration for Rastrigin function
clonalg = Clonalg(
problem_size=problem_size,
N=50,
selection_size=15,
rate_clonal=10,
rate_hypermutation=0.3,
n_diversity_injection=15,
bounds=bounds,
seed=1234
)
# Register the fitness function
clonalg.register('affinity_function', rastrigin_fitness)
Running the optimization
clonalg.optimize(100, 20)
if clonalg.best_cost is not None:
print('Best cost:', abs(clonalg.best_cost))
Output:
┌───────────┬─────────────────────────┬────────────────────┬─────────────────┐
│ Iteration │ Best Affinity (min) │ Worse Affinity │ Stagnation │
├───────────┼─────────────────────────┼────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ 1 │ 7.153385│ 76.021342│ 0 │
│ 2 │ 2.344533│ 33.315827│ 0 │
│ 3 │ 2.140116│ 30.948129│ 0 │
│ 4 │ 2.140116│ 31.998642│ 1 │
│ 5 │ 0.484366│ 56.071764│ 0 │
│ 6 │ 0.185833│ 36.260411│ 0 │
│ 7 │ 0.185833│ 27.861454│ 1 │
│ 8 │ 0.185833│ 29.599095│ 2 │
│ 9 │ 0.185833│ 17.182111│ 3 │
│ 10 │ 0.185833│ 18.465362│ 4 │
│ 11 │ 0.185833│ 56.496717│ 5 │
│ 12 │ 0.161393│ 33.675148│ 0 │
│ 13 │ 0.161393│ 22.855341│ 1 │
│ 14 │ 0.161393│ 71.552278│ 2 │
│ 15 │ 0.161393│ 43.872058│ 3 │
│ 16 │ 0.161393│ 28.045742│ 4 │
│ 17 │ 0.161393│ 46.444268│ 5 │
│ 18 │ 0.161393│ 28.197926│ 6 │
│ 19 │ 0.030122│ 32.764169│ 0 │
│ 20 │ 0.030122│ 27.485715│ 1 │
│ 21 │ 0.030122│ 17.547005│ 2 │
│ 22 │ 0.030122│ 43.293872│ 3 │
│ 23 │ 0.030122│ 43.366562│ 4 │
│ 24 │ 0.030122│ 42.037080│ 5 │
│ 25 │ 0.030122│ 28.196466│ 6 │
│ 26 │ 0.020278│ 37.645191│ 0 │
│ 27 │ 0.020278│ 28.413549│ 1 │
│ 28 │ 0.020278│ 32.007209│ 2 │
│ 29 │ 0.020278│ 45.392869│ 3 │
│ 30 │ 0.020278│ 15.223606│ 4 │
│ 31 │ 0.020278│ 46.298146│ 5 │
│ 32 │ 0.020278│ 21.641321│ 6 │
│ 33 │ 0.020278│ 47.343886│ 7 │
│ 34 │ 0.020278│ 20.720949│ 8 │
│ 35 │ 0.020278│ 31.158014│ 9 │
│ 36 │ 0.020278│ 42.655313│ 10 │
│ 37 │ 0.020278│ 28.978964│ 11 │
│ 38 │ 0.020278│ 27.926847│ 12 │
│ 39 │ 0.020278│ 22.639969│ 13 │
│ 40 │ 0.020278│ 43.618425│ 14 │
│ 41 │ 0.020278│ 28.637045│ 15 │
│ 42 │ 0.020278│ 36.324186│ 16 │
│ 43 │ 0.020278│ 58.068571│ 17 │
│ 44 │ 0.020278│ 61.189833│ 18 │
│ 45 │ 0.020278│ 26.157713│ 19 │
│ 46 │ 0.020278│ 49.301933│ 20 │
└───────────┴─────────────────────────┴────────────────────┴─────────────────┘
Total time: 0.079153 seconds
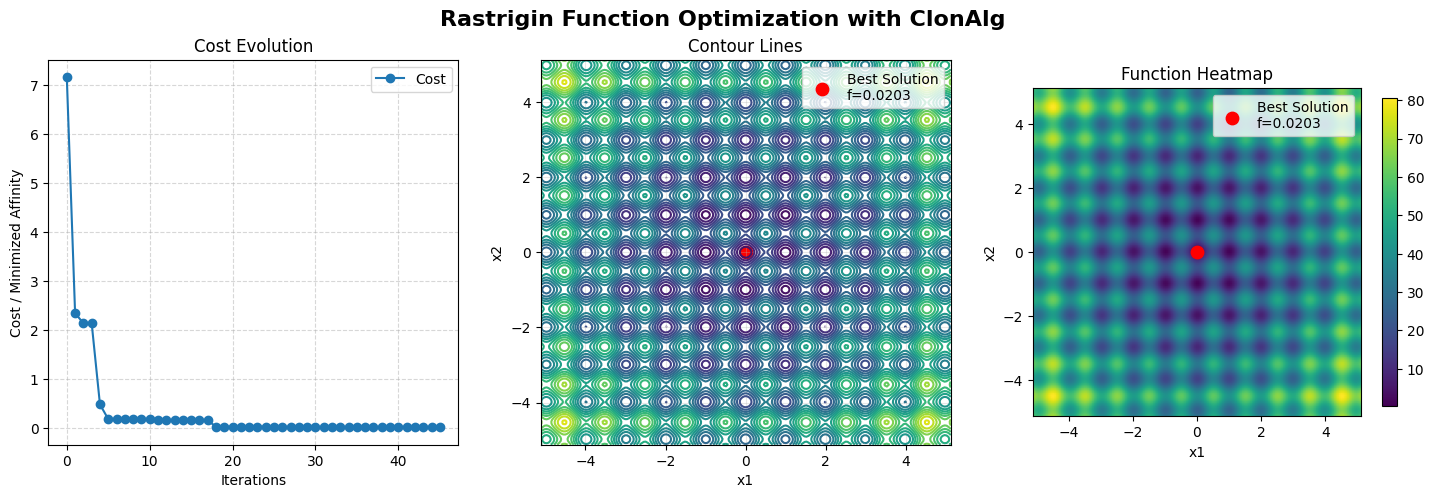
Best cost: 0.020278270044883584
Result
print(clonalg.get_report())
Output:
=============================================
Optimization Summary
=============================================
Best cost : 0.020278270044883584
Best solution : [ 0.0088594 -0.00487301]
Cost History per Iteration:
┌────────────┬────────────────────────────┐
│ Iteration │ Cost │
├────────────┼────────────────────────────┤
│ 1 │ 7.153385 │
│ 2 │ 2.344533 │
│ 3 │ 2.140116 │
│ 4 │ 2.140116 │
│ 5 │ 0.484366 │
│ 6 │ 0.185833 │
│ 7 │ 0.185833 │
│ 8 │ 0.185833 │
│ 9 │ 0.185833 │
│ 10 │ 0.185833 │
│ 11 │ 0.185833 │
│ 12 │ 0.161393 │
│ 13 │ 0.161393 │
│ 14 │ 0.161393 │
│ 15 │ 0.161393 │
│ 16 │ 0.161393 │
│ 17 │ 0.161393 │
│ 18 │ 0.161393 │
│ 19 │ 0.030122 │
│ 20 │ 0.030122 │
│ 21 │ 0.030122 │
│ 22 │ 0.030122 │
│ 23 │ 0.030122 │
│ 24 │ 0.030122 │
│ 25 │ 0.030122 │
│ 26 │ 0.020278 │
│ 27 │ 0.020278 │
│ 28 │ 0.020278 │
│ 29 │ 0.020278 │
│ 30 │ 0.020278 │
│ 31 │ 0.020278 │
│ 32 │ 0.020278 │
│ 33 │ 0.020278 │
│ 34 │ 0.020278 │
│ 35 │ 0.020278 │
│ 36 │ 0.020278 │
│ 37 │ 0.020278 │
│ 38 │ 0.020278 │
│ 39 │ 0.020278 │
│ 40 │ 0.020278 │
│ 41 │ 0.020278 │
│ 42 │ 0.020278 │
│ 43 │ 0.020278 │
│ 44 │ 0.020278 │
│ 45 │ 0.020278 │
│ 46 │ 0.020278 │
└────────────┴────────────────────────────┘
Evolution of the best over generations